Dietary protein is an essential nutrient that is vital for our overall health and well-being. How much protein do you need on a keto diet, and how can you make sure to get the right amount? Read on to learn all about protein and different ways to meet your daily target.
Why Protein Is Important
Protein is made up of amino acids, often called the “building blocks” of protein. Amino acids play several crucial roles in the body, including:
- Muscle growth and repair: The protein in your muscles is continuously broken down and rebuilt daily. A steady supply of amino acids is essential for muscle protein synthesis, meaning the creation of new muscle.
- Hormone production: Several hormones that help regulate metabolism and other functions –– such as insulin and thyroid hormone –– are made from amino acids.
- Immune system support: Amino acids aid in immune function by helping activate immune cells and producing antibodies.
Of the 20 amino acids that make up protein, nine are considered essential, meaning you must get them from your diet.
Because animal foods (meat, seafood, eggs, and dairy) contain optimal amounts of all the essential amino acids, their protein is considered “complete.” While many plant foods contain all nine essential amino acids, one or more is often only present in very small quantities, with the exception of soy, which is considered complete. In addition, the protein in plants typically isn’t digested and absorbed as easily as protein from animal sources. Therefore, the protein in most plants is considered “incomplete.”
In addition, collagen, which comes from animal bones and skins, is not considered a complete protein because it is mainly made up of nonessential amino acids, contains smallamounts of several essential amino acids, and does not contain any of the essential amino acid tryptophan. However, collagen is still beneficial for skin, gut, and joint health, due to its high content of the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. So including collagen in your diet is healthful, but it shouldn’t be one of the main protein sources in your diet.
How Much Protein Do You Need on a Ketogenic Diet?
The amount of protein you need is based on your weight (specifically, your lean mass), age, activity level, and health goals.
To achieve and maintain nutritional ketosis, it’s important to get enough protein, but not too much. Consuming more protein than you need can cause your pancreas to release more insulin to help muscles take up the additional amino acids, which can reduce ketone production in the liver. As a result, eating more protein than you need may lower your ketone levels.
On a ketogenic diet, it’s best to aim for about 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of reference body weight per day. By using your reference body weight, you’ll be basing your protein target on your estimated lean body mass rather than your total body weight. You can find your reference body weight on this chart from Virta Health.
For example, if your reference weight is 145 pounds (66 kilograms), you should aim for about 79 to 132 grams of protein per day, which you’ll get by consuming 11 to 19 ounces (310 to 535 grams) of protein food, such as meat, fish, eggs, or cheese. (One ounce or 28 grams of protein food contains approximately 7 grams of protein).
That’s a pretty big range, isn’t it? As a starting point, you may want to aim for the middle of the range: 1.5 grams per kilogram. For the example above, that would be 99 grams of protein per day, or about 14 ounces of protein food by weight.
Some people may be able to eat more protein than this and still maintain nutritional ketosis. If you want to try eating more protein, test your ketone levels at different time points to see how higher protein intake affects you.
Studies suggest that it’s best to spread protein intake out among two or three meals per day to optimize protein synthesis. In the case above, that would mean eating about 30-35 grams of protein three times a day or about 50 grams of protein twice a day. Someone with a lower reference weight who chooses to eat 1.2 grams of protein per kilogram might only need 20 to 25 grams of protein three times a day.
Additionally, modern research demonstrates that concerns about potential negative effects of higher protein on kidney and bone health appear to be misguided. Indeed, even people with chronic kidney disease may be able to tolerate higher amounts of protein than was previously thought.
Importantly, the recommendations above are for people who want to improve their metabolic health or lose weight. Individuals with cancer, epilepsy, or neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease may need less protein and more fat, such as a 3:1 or 4:1 therapeutic ketogenic diet. However, people who follow therapeutic ketogenic diets for these conditions should work with a doctor and/or registered dietitian who can determine their protein needs and monitor their safety and progress.
Protein In Keto-Friendly Foods
One ounce (28 grams) of meat, poultry, seafood, or cheese provides about 7 grams of protein. One large egg also provides 7 grams of protein.
You can get 25-30 grams of protein by consuming the foods below or a combination of them, such as 2 ounces (56 grams) of meat and 2 ounces of cheese:
- 4 ounces (114 g) of cooked meat, poultry or seafood (about the size of a cell phone)
- 4 eggs
- 4 ounces (114 g) of cheese (about the size of a cell phone)
- 1 cup (225 g) of full-fat Greek yogurt
- 1 cup (230 g) of full-fat cottage cheese
- 1 cup (250 g) of tofu
- 1.5 cups (235 g) of edamame
Nuts and seeds provide about 3 to 7 grams of protein per ounce (about 28 grams). However, since their protein isn’t considered complete, they shouldn’t be the sole source of protein in a meal.
In addition, you’ll get small amounts of protein from non-starchy vegetables. One cup of greens and other keto-friendly vegetables contains about 2 to 4 grams of protein.
Meeting Your Daily Protein Needs on Keto
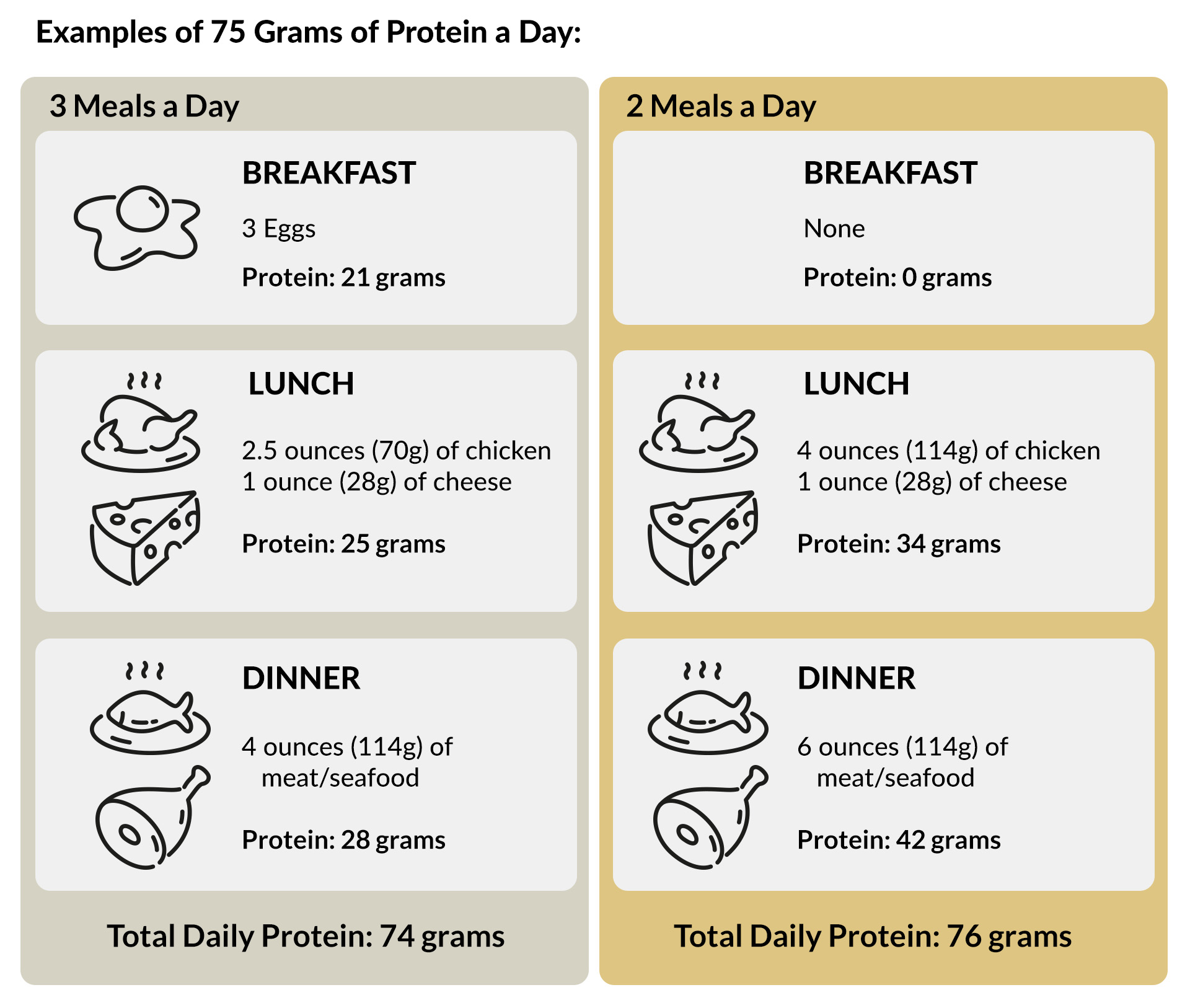
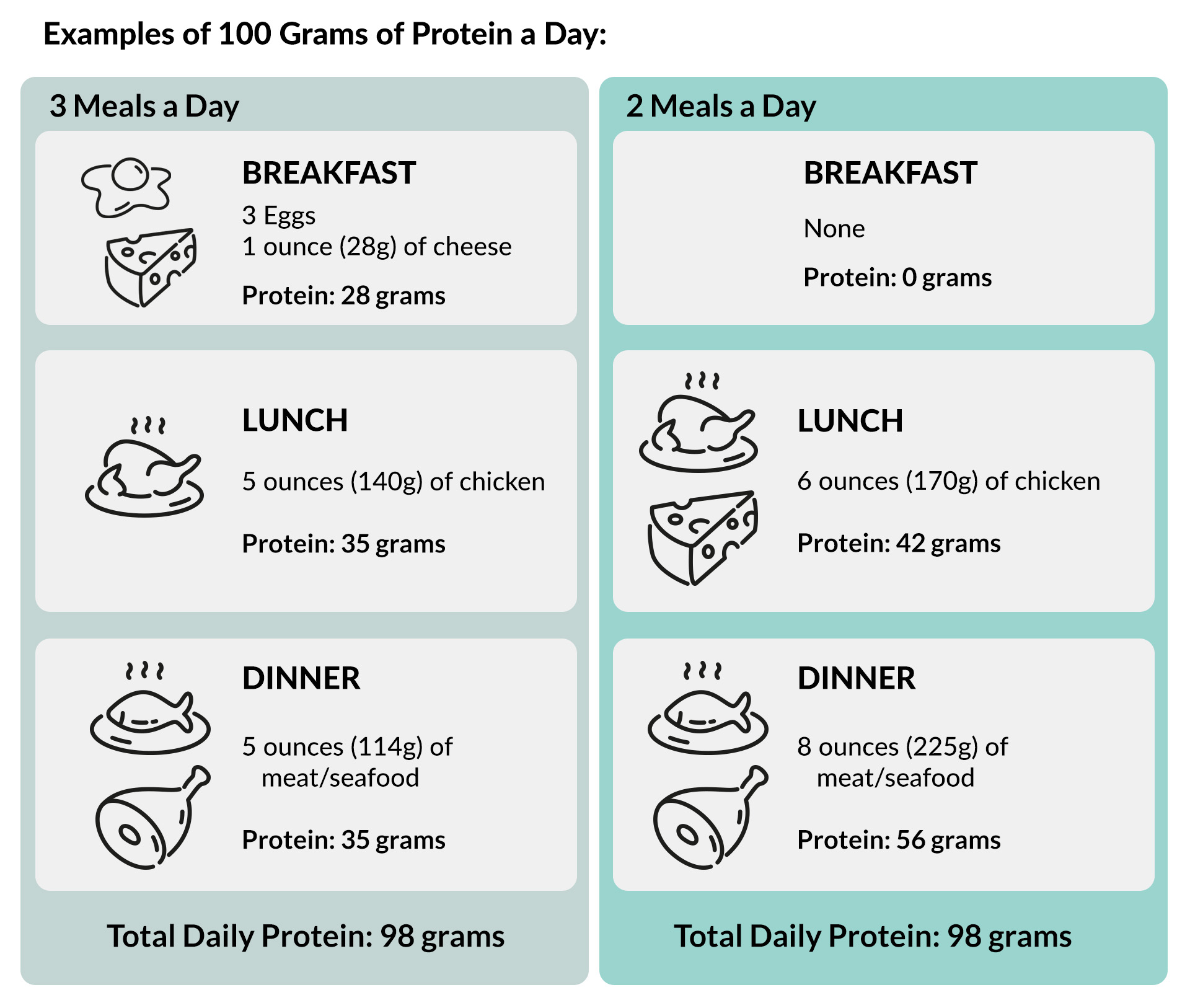
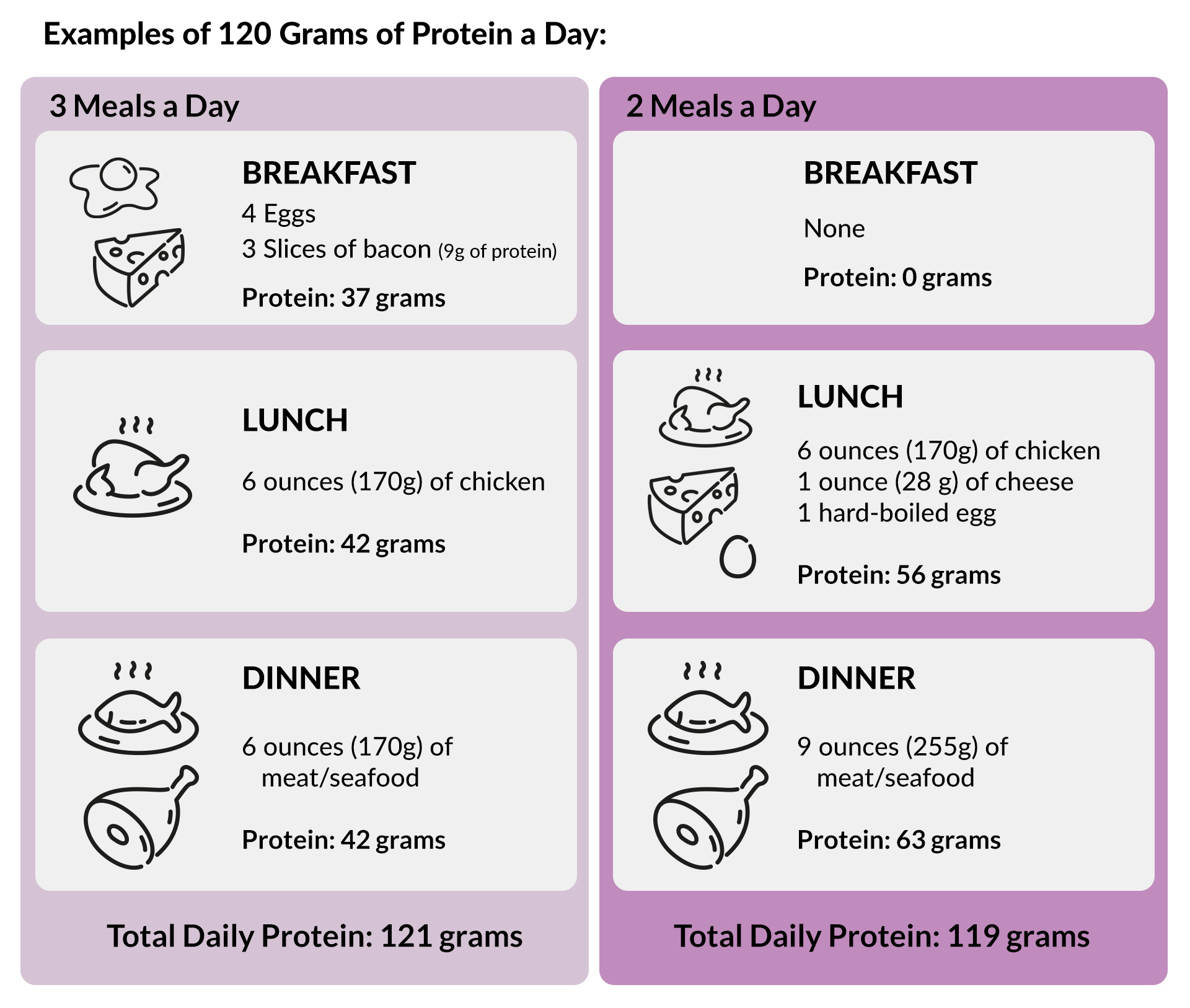
Once you’ve figured out how much protein you need for the day, you’ll know how much to aim for at each meal. Here are some ideas for meeting different daily protein targets when eating two meals or three meals per day.
Note: Protein content is approximate.
This is just the main protein portion of your meal. Remember, you’ll get about 2 to 4 grams of protein per cup of non-starchy vegetables. And be sure to add some healthy fat, such as olive oil, butter, or cream. Although fat doesn’t provide protein, it will add flavor, mouthfeel, and satiety to your meals.
Here are a few ideas and recipes for inspiration:
- Chicken salad: 3 ounces of grilled chicken, 1 cup of leafy greens with olive oil and vinegar dressing: 26 grams of protein
- Cottage cheese with nuts: 1 cup of full-fat cottage cheese with 1 ounce of chopped pecans: 30 grams of protein
- Tofu stir-fry: 5 ounces of tofu, ½ cup of cabbage, ½ cup of snow peas sauteed in sesame oil: 35 grams of protein
- Steak with Brussels sprouts: 6 ounces of grilled steak, 1 cup of Brussels sprouts roasted in olive oil or butter: 47 grams of protein
- Salmon filet with cream sauce and broccoli: 8 ounces of grilled salmon with cream sauce and 1 cup of broccoli: 60 grams of protein
- Keto Shrimp Louis: 24 grams of protein
- Low Carb Breakfast Egg Cups: 29 grams of protein
- Pork Tenderloin with Asian Mushrooms: 40 grams of protein
- Creamy Keto Chipotle Chicken with Spinach and Lime-Cilantro “Rice”: 43 grams of protein
- Keto Caprese Salmon Skewers: 65 grams of protein
Key Takeaway
Incorporating adequate protein into your ketogenic lifestyle is important, and it’s easy to do when you include a moderate amount of high-quality protein at each meal. By focusing on minimally processed, nutrient dense foods and getting the amount of protein you need, you’ll help set yourself up for long-term keto success.
Note: Be sure to speak with your doctor or other health care provider before starting a ketogenic diet and follow up regularly thereafter. This is especially important if you take any medications or have a medical condition.