Rejoice! Now that you’re on a high-fat, low-carb diet, you can emphatically say, “Pass the butter” or “Extra salad dressing, please!”— even if your goal is weight loss.
In fact, butters and oil –– both of which are predominantly fat –– are an important part of keto cuisine and its health benefits. But they’re not all created equal. Some oils are good tools for helping you stay in ketosis; you’ll want to make these healthy fats a regular part of your diet. Others you’ll want to avoid. Today we share basics on what you need to know about these ingredients/condiments.
It’s not hard to transition from using all kinds of cooking fats to just those that are keto-friendly. In fact, if you cook at all, you probably already have some perfect options in your kitchen. Take a look at the following keto-friendly choices, and reach for them when you need to cook, make a dressing, or finish a dish with a drizzle of oil or a smear of butter.
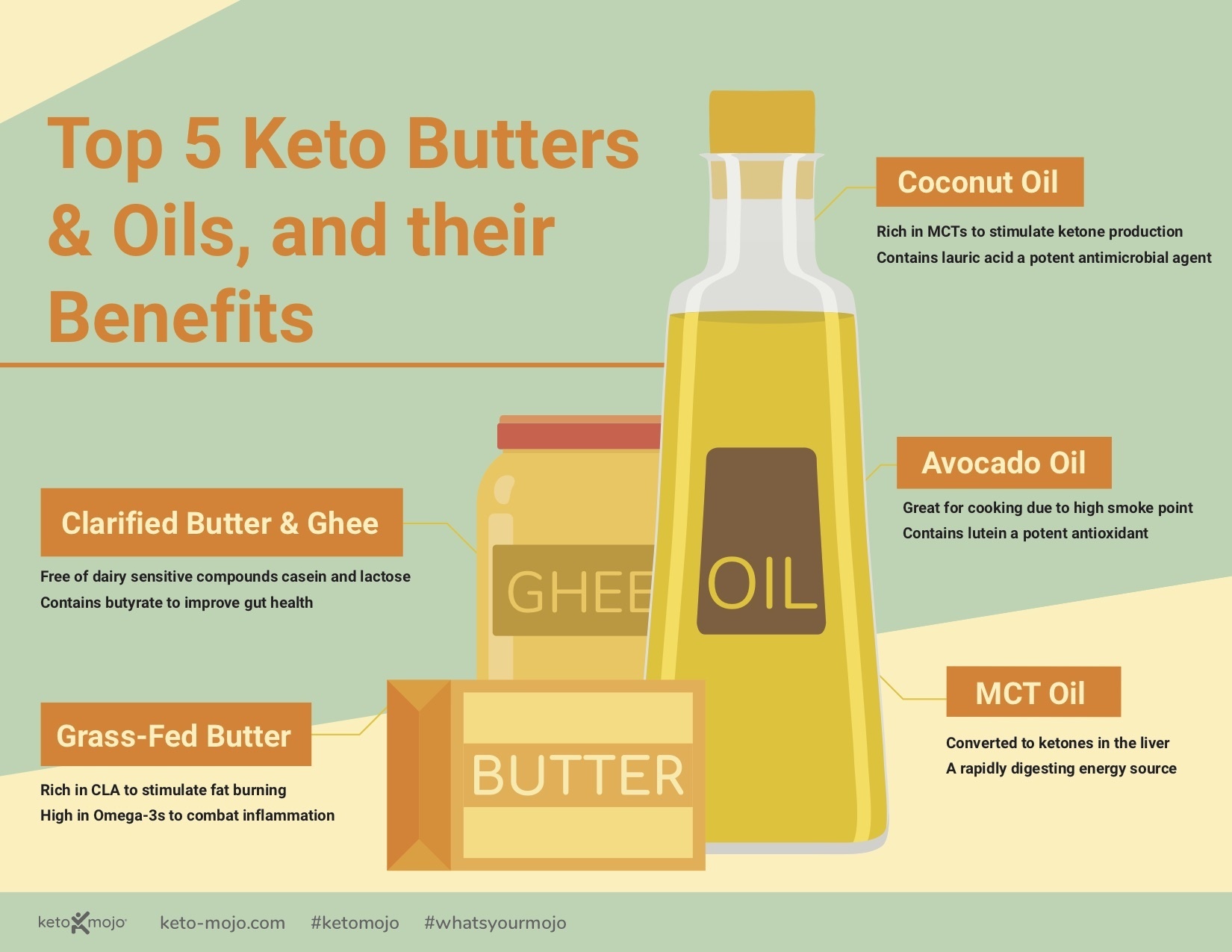
Butter
It’s a big thumbs up for butter, especially grass-fed butter, on the ketogenic diet as it contains only trace amounts of carbs per serving whether it’s salted or unsalted. Like other fatty dairy products, butter is rich in conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), the fatty acid that may promote fat loss and potentially reduce the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease. Grass-fed butter contains up to five times more CLA than butter from grain-fed cows and is much higher in Omega-3 fatty acids. Use it for cooking keto meals, baking keto recipes, or in your bulletproof coffee, or spread it generously when you need more fat. The classic French snack of radishes with butter and flaky salt? Totally keto and delicious!
Butter Nutritional Information: 1 Tbsp: 102 Calories, 12g Fat, 0g Carbs, 0.1g Protein
Clarified Butter and Ghee
Clarified butter and ghee are essentially butter with the milk solids removed; they’re comprised almost exclusively of fat, most of which is saturated fat.
Clarified butter is made by heating butter, removing it from the heat after the butterfat and milk solids separate, then skimming away and discarding the milk solids. Ghee, the Hindi word for “fat,” is butter that’s been cooked a bit longer to allow the milk solids to caramelize and produce a deeper golden color and distinct nutty flavor before they’re skimmed and discarded. In both instances, what’s left is pure butterfat, which can be enjoyed and used the same way you’d use butter. Because ghee separates milk from fat, this butter substitute is lactose-free, making it better than butter if you have allergies or sensitivities to lactose.
Since both clarified butter and ghee don’t contain quick-to-spoil liquid and milk components, they have longer shelf lives, which is part of the reason they’re staples in hot countries. Plus, they have much higher smoke points than butter, which makes them awesome for cooking.
Store-bought ghee can be expensive and is less common in grocery stores, so many ketonians make it at home. The recipe is easy. See for yourself here.
Clarified Butter and Ghee Nutritional Information: 1 Tbsp: 112 Calories, 13g Fat, 0g Net Carbs, 7.9g Protein
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil has unique properties that make it a rockstar for keto cooking. Specifically, it’s rich in medium-chain triglycerides (at about 50%), which can increase ketone production and may increase metabolic rate and promote the loss of weight and belly fat. It’s solid at room temperature like other mostly saturated fats (e.g., butter). Coconut oil can be substituted in equal amounts for any oil; however, when substituting it for a solid fat, such as butter or lard, use 25% less coconut oil than the recipe calls for.
Want to try a recipe using coconut oil for frying? Try our tasty recipe for Keto Koconut Chicken Tenders!
Coconut Oil Nutritional Information: 1 Tbsp: 121 Calories, 13g Fat, 0g Net Carbs, 0g Protein
Avocado Oil
Avocado oil is simply oil pressed from avocados. High in monounsaturated fats, it’s very healthy, as 70% of it is oleic acid. Add that it has mild flavor and a high smoke point (the point at which the oil begins to burn and its smell and taste is altered), and you can understand why it’s a staple in keto cooking. Use this versatile oil in dressings, marinades, and sautés, as well as in recipes for homemade mayonnaise.
Avocado Oil Nutritional Information: 1 Tbsp: 124 Calories, 14g Fat, 0g Net Carbs, 0g Protein
MCT Oil
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) or medium-chain fatty acids are fats most often derived from coconut oil, palm oil, or a mixture of the two. MCT oil comes in liquid form and is colorless, odorless, and stays liquid at room temperature, making it the perfect fat to add to food, smoothies, and coffee for extra energy. Because the oil is quickly and easily converted by the liver into ketones, it is a darling of keto lifestyles. But it should be used with care and gradually increased over time, as excess consumption may cause a stomachache and diarrhea.
With a relatively low smoke point and reason for moderation, MCT oil is ideal for use in salad dressings and in relatively low-temperature baking. With its neutral flavor, it can be paired with a wide range of ingredients and flavors. Chocolate Peanut Butter Fat Bombs use MCT oil and are awesome, so give ‘em a try!
MCT Oil Nutritional Information: 1 Tbsp: 121 Calories, 13g Fat, 0g Net Carbs, 0g Protein
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil
Versatile and multifunctional, extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO) is a cold-pressed, heart-healthy oil that contains oleic acid along with many antioxidants. Cooking with EVOO has never been easier (or tastier)! Try drizzling it over salad with a few hard-boiled eggs for protein, stirring it into a hearty stew or soup for added flavor, sauté veggies with it, or simply use it as a delicious addition to sliced avocado, sliced tomato, or other keto snacks.
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Nutritional Information: 1 Tbsp: 120 Calories, 14g Fat, 0g Net Carbs, 0g Protein
Lard
It may be less commonly used in today’s everyday cooking, but lard, or rendered pork fat, is a great choice on a keto diet. It functions similarly to butter, providing flavor, crispness, flakiness and tenderness to baked goods, but has a much stronger flavor. Lard can also be used for sautéing, making sauces such as Bearnaise, and making dips such as bacon mayonnaise.
Lard Nutritional Information:1 Tbsp: 115 Calories, 13g Fat, 0g Net Carbs, 0g Protein
Tallow
Tallow is rendered animal fat, usually from beef. It’s comprised of approximately 50% saturated fat, 42% monounsaturated fat, and only 4% polyunsaturated fat and is great for high-heat cooking. Store-bought tallow can be expensive and is often hydrogenated, so if you’re inclined, you can easily make your own.
Tallow Nutritional Information:1 Tbsp: 115 Calories, 13g Fat, 0g Net Carbs, 0g Protein
Duck Fat
When you hear the term “duck fat” you may think it’s a gourmet ingredient used only in fancy French restaurants. But duck fat doesn’t have to be reserved for special occasions or elegant preparations. Made from one single ingredient, the natural fat from ducks, it’s usually rendered and filtered to make sure the fat is pure, providing outstanding flavor to just about any dish, from green vegetables to grass-fed steaks.
Duck Fat Nutritional Information: 1 Tbsp: 113 calories, 13g Fat, 0g Net Carbs, 0g Protein
Oils to Avoid
Oils that go through intense processing generally include processed trans fats that may be damaging to overall health. Thus, we recommend avoiding the following oils:
- Canola
- Cottonseed
- Grapeseed
- Rice bran
- Sesame
- Soybean
- Sunflower
- Safflower
Mojo On!
Now that you’re armed with better knowledge of which fats to cook with, try using them when you sauté, fry, or bake. Before you know it, you’ll be easily cooking keto!