Going keto is all about change. Changing your diet. Changing your metabolism. Even changing your hormone levels.
Take the hormone testosterone. Testosterone (T) is known as the male sex hormone—but females have a fair bit of it too. Men, in particular, rely on testosterone to burn fat, build muscle, grow bone, and stay sexually healthy.
In this article, you’ll learn the signs of low levels of testosterone, how diet and exercise affect testosterone levels, and—yes—the answer to the $64,000 question: can the keto diet boost low testosterone levels? Read on.
What Is Testosterone?
Testosterone is a steroid hormone—a chemical messenger that gives orders to your cells.
Grow, says testosterone to bone and muscle cells. Burn, says testosterone to fatty acids in your blood. And so they do.
Men have about 15 times more circulating testosterone than females. In fact, many functions of testosterone, such as regulating sperm production, are male-specific.
But women depend on testosterone too. Suprisingly enough, testosterone is the most abundant sex hormone in the female body—even moreso than estrogen levels!
Testosterone, you’ve probably heard, is an anabolic hormone. This simply means that high amounts of T promote growth in muscle, bone, and even red blood cells.
An exception to the testosterone equals growth rule? Fat.
That’s right. Unlike estrogen, testosterone helps you oxidize (burn) rather than store lipids.
Low Testosterone Symptoms
After age 30 or so, testosterone drops significantly with each passing decade. As you might expect, men experience these drops more acutely than women.
Besides aging, other causes of lower testosterone levels include drugs, chemotherapy, testicular disease, and genetic disorders like Klinefelter syndrome.
Here are the Symptoms of Low Testosterone:
- Increased body fat
- Lower bone density
- Loss of muscle mass
- Lower libido
- Decreased red blood cell production (possible anemia)
- In men, decreased testicle size
If you or your doctor notice any of these symptoms, consider testing your testosterone levels.
Testosterone Testing
There are three main methods for testing testosterone:
- Blood testing: Total serum testosterone is best measured between 8 AM and 10 AM. Anywhere from 300 nanograms per deciliter to 900 nanograms per deciliter is generally considered normal. Depending on the results, your doctor may follow up by testing follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) two key sex hormones involved in testosterone production.
- Saliva testing: Though less studied than blood testing, some research suggests salivary testosterone is a valid measure.
- Urine testing: The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) has used urine tests for decades to monitor testosterone abuse in Olympic athletes. The DUTCH test is a popular option available on the market.
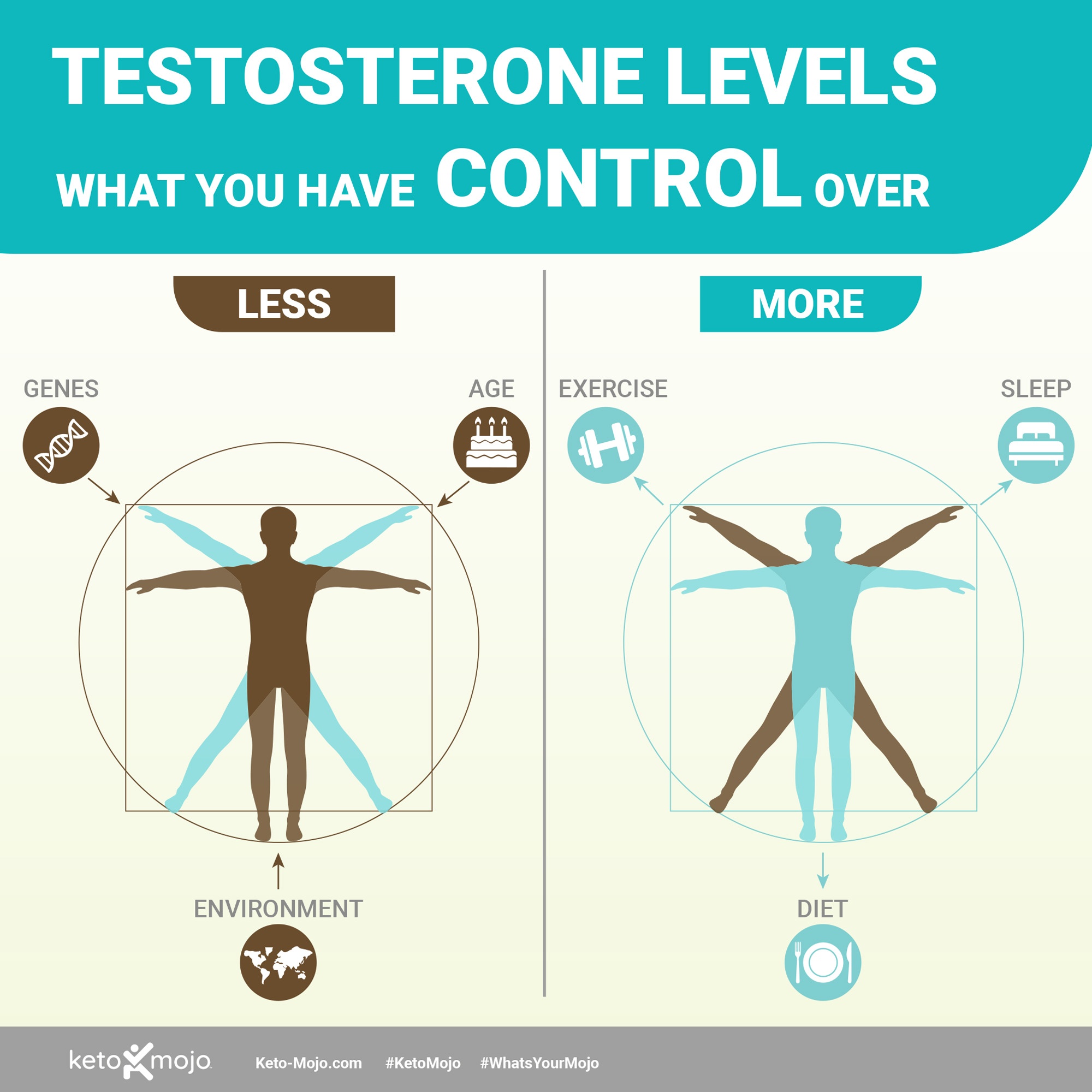
What Affects Testosterone?
Testosterone production is a big bag of complexity. Welcome to the human body.
Genes, age, and environment – all of them determine testosterone levels. Many of these factors aren’t within your control.
But one is within your control: how you live your life.
Take sleep, for instance. In one study, one week of sleep restriction (five hours per night) decreased daytime testoterone levels by 10 to 15 percent in healthy young men.
So yes. Your sex drive is determined, in part, by your sleep habits.
Exercise is another big one. Both weight training and high intensity interval training (HIIT) have been shown to boost testosterone levels.
Now then. On to diet.
Diet and Testosterone
When it comes to diet and testosterone, there are two main levers you can pull:
- How much you eat
- The macronutrient composition (carbs, protein, fat) of your diet
First, calories matter. Long-term calorie restriction, it’s been shown, not only reduces bone density and muscle mass, but also reduces testosterone levels.
But there’s a caveat. Temporarily cutting calories to lose weight can boost testosterone. This has been shown in obese men. Why? For one, losing weight increases insulin sensitivity, which helps leydig cells (testosterone-producing cells in testicles) produce testosterone in the testes.
What you eat also affects your T levels. For instance, higher carb intake appears to prevent testosterone from plummeting after intense exercise. But other research suggests that high-fat diets outperform high-carb diets for muscle building and testosterone production.
Can A Keto Diet Raise Testosterone Levels?
You’ve heard of the ketogenic diet. It’s a low-carb diet that has you eating about 75 percent of calories from fat. The rest is protein. Carbs are minimized. And yes, early research of the overall health benefits indicates that going keto can raise testosterone.
Researchers split 25 young men into two diets – keto and high-carb – then had both groups resistance train for 11 weeks. The results were interesting. The keto dieters not only had greater reductions in fat mass, but also had significant bumps in total testosterone.
When you see a 118 nanogram per deciliter increase in 11 weeks, that’s enough to take someone that’s considered ‘low testosterone’ into significantly higher testosterone and within normal range. – Celebrity Health Coach Thomas DeLauer,
Okay, so one result doesn’t prove keto is the ultimate testosterone diet. But it does suggest that keto is compatible with healthy T.
Why, exactly, keto raises testosterone isn’t obvious. The mechanism likely involves the much-maligned molecule known as cholesterol. Think of cholesterol as raw material for testosterone production. More raw materials in, more testosterone out.
Here’s the thing. With all those healthy fats, the keto diet is incredibly rich in cholesterol. From the perspective of testosterone, this is a good thing.
And no. According to the science, dietary cholesterol does not raise your risk for heart disease. That myth has been debunked.
The Final Word
Time for a quick recap of this learning session.
- Testosterone helps you build muscle, grow bone, and burn fat.
- Low testosterone (often due to aging) presents as brittle bones, muscle loss, low sex drive, and fat gain.
- Testosterone can be measured in blood, saliva, or urine.
- Sleep and exercise help boost testosterone.
- Calorie restriction lowers testosterone, except during healthy weight loss.
- A keto diet has been shown to increase testosterone levels more than a high-carb diet.
- High-fat diets are high in cholesterol, the building block of testosterone.
Want to know how keto is impacting your testosterone? Measure it. See how you feel, and consider getting a test. Tracking your biomarkers seems like a lot at first—but it’s how you measure change in your body. So have fun with it, and use that data to level up your health.
Regardless, whenever trying a new diet, be sure to consult your primary care physician for medical advice on whether the diet is a good fit for you.